The Potential Return Advantage of Stacking Managed Futures on Equities
Overview
With the majority of active managers failing to outperform over time, financial advisors are increasingly looking for alternative ways to enhance portfolio returns. Return stacking – layering managed futures on top of a traditional equity allocation – provides a structural path to seeking outperformance without sacrificing equity exposure. This article explores the potential benefits of a 100% stocks + 100% managed futures approach, which has historically improved risk-adjusted returns and reduced drawdowns during crisis periods. Learn how capital-efficient strategies like return stacking could redefine how advisors think about diversification and return enhancement.
Key Topics
How Financial Advisors Can Use Stacking to Pursue Higher Returns
Achieving consistent outperformance in public markets is one of the greatest challenges faced by financial advisors. The SPIVA Scorecard consistently shows that the vast majority of active equity managers fail to outperform their benchmarks over the long term. According to the 2023 SPIVA U.S. Scorecard, over 90% of large-cap equity funds underperformed the S&P 500 over a 20-year period. Similarly, Morningstar’s Active/Passive Barometer has repeatedly highlighted that very few managers persistently generate excess returns.
Given the difficulty of finding persistent alpha through security selection, advisors need alternative approaches to enhance portfolio returns. Return stacking – adding managed futures on top of a traditional equity allocation – offers an alternative approach to pursuing outperformance. By leveraging the benefits of capital-efficient instruments, investors can access multiple sources of return while maintaining full equity exposure.
The Return Stacking Framework
Consider a return stacked® portfolio that seeks to provide $1 of exposure to equities plus $1 of exposure to managed futures for every $1 invested. Unlike traditional attempts at outperformance, which rely on stock-picking or timing the market, the return stacking strategy provides an additional return stream through systematic trend-following strategies, commonly found in managed futures.
For example, instead of allocating 80% to equities and 20% to managed futures, an investor can maintain a 100% equity allocation while adding a full 100% overlay of managed futures. This approach ensures that the investor does not have to sacrifice equity beta to introduce an alternative return source.
Why Pursue Outperformance Through Return Stacking?
- The Challenge of Finding Traditional Alpha: Active managers struggle to beat benchmarks, and when they do, success rarely persists. By contrast, systematic strategies like managed futures have historically demonstrated resilience and the ability to generate uncorrelated returns over time.
- Capital Efficiency Without Reducing Equity Exposure: Unlike traditional alternatives that require reducing stock (or bond) holdings to make room in a portfolio, return stacking may allow advisors to enhance portfolios without sacrificing upside potential from equities.
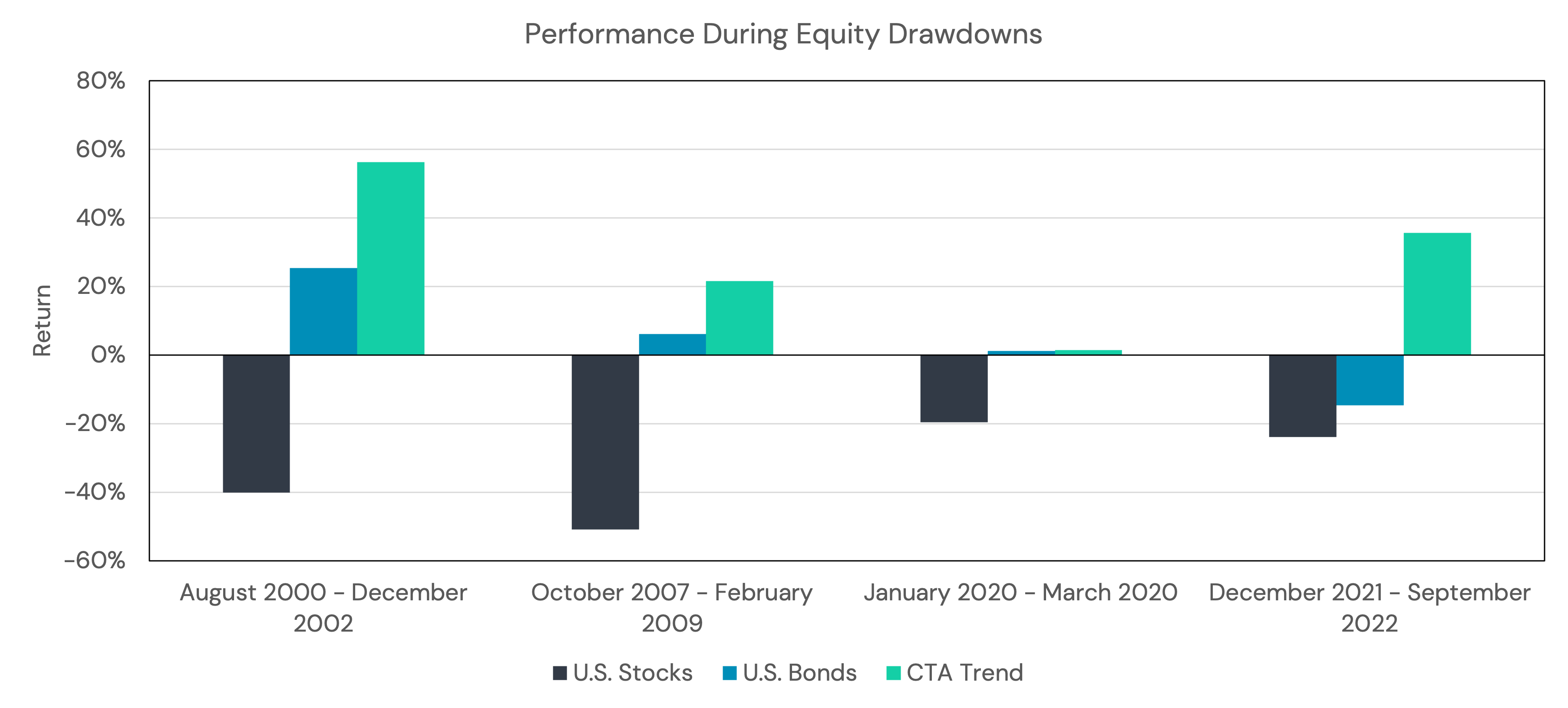
- Historical Outperformance During Crisis Periods: Managed futures strategies have historically demonstrated positive returns during major equity downturns because they capitalize on sustained trends – whether in equities, interest rates, or commodities. This has allowed them to generate positive returns during periods when equities suffered significant losses, making them a strong candidate for inclusion in portfolios seeking long-term outperformance.
Historical Performance: Stocks vs. Return Stacked® Portfolios
| Period | S&P 500 Total Return |
Managed Futures | 100% Stocks + 100% Managed Futures |
| 2000-2002 (Dot-com Crash) | -37.6% | +40.8% | -16.6% |
| 2008 (Financial Crisis) | -37.0% | +20.9% | -23.3% |
| 2022 (Rising Rates) | -18.1% | +27.4% | +5.0% |
Register for our Advisor Center
Tools Center:
Easily backtest & explore different return stacking concepts
Model Portfolios:
Return stacked allocations, commentary and guidance designed
for a range of client risk profiles and goals
Future Thinking:
Receive up-to-date insights into the world of return stacking theory and practice
Comparing Return Stacking to Other Approaches
| Strategy | Goal | Historical Success Rate |
| Stock-Picking (Traditional Active Management) | Outperform benchmark via security selection | <15% success rate over 15 years (SPIVA) |
| Factor Investing | Capture excess returns via factors like value/momentum | Mixed results, strong cyclicality |
| Return Stacking (100% Stocks + 100% Managed Futures) | Enhance returns while maintaining full equity exposure | Historically strong during crises, potential for smoother long-term compounding |
How Return Stacking Works in Practice
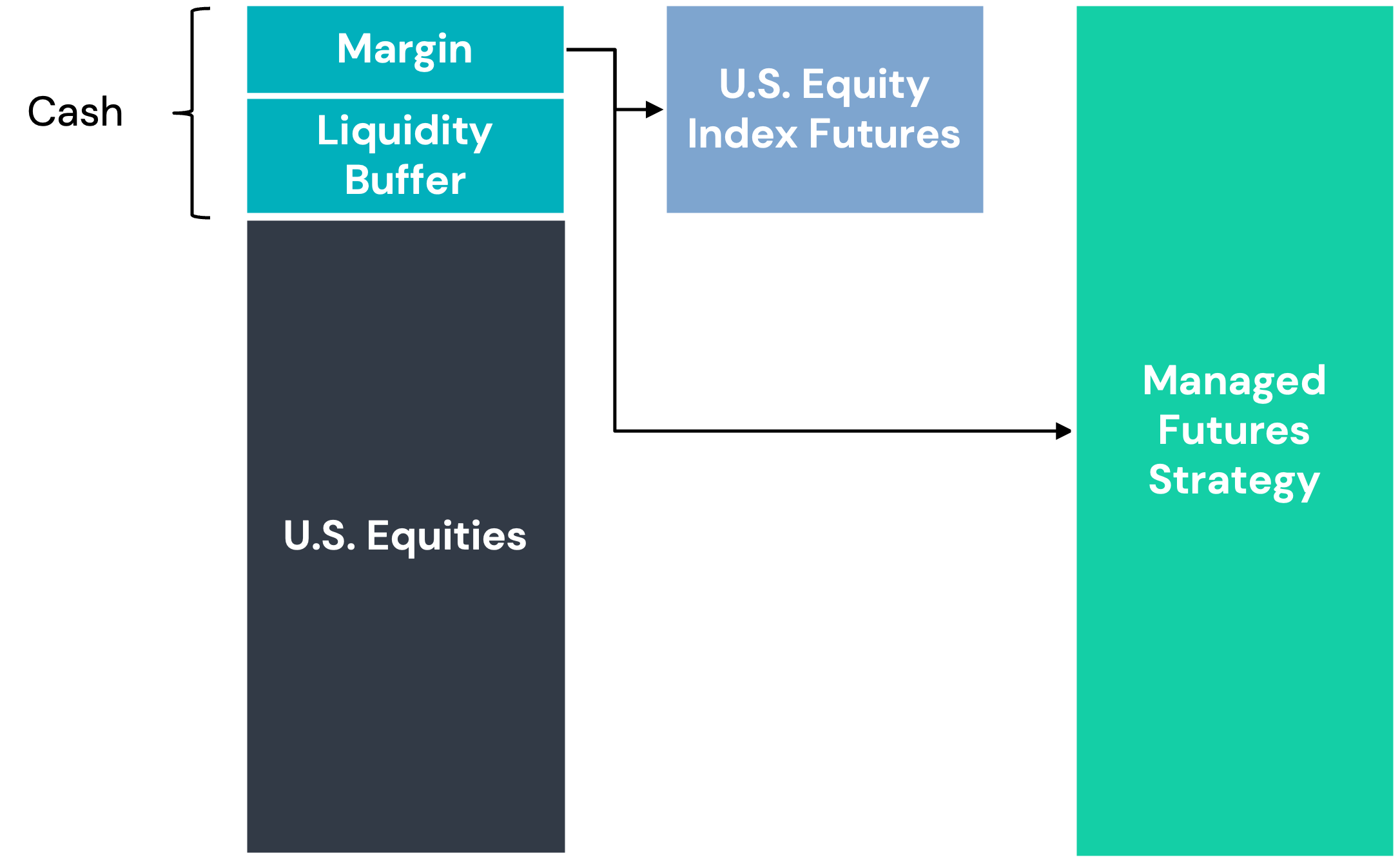
Return stacking can be implemented using capital-efficient vehicles such as ETFs or mutual funds that provide exposure to both equities and managed futures within a single allocation. These funds use a combination of futures contracts and collateralized investments to achieve notional exposure beyond 100% of an investor’s capital.
For example, a return stacked® strategy may hold:
- 100% exposure to U.S. large-cap equities via underlying equities or index futures.
- 100% exposure to a diversified managed futures strategy through trend-following futures contracts.
- A liquidity reserve consisting of short-term U.S. Treasuries or cash equivalents to manage margin requirements.
Why Managed Futures as the Overlay?
Unlike alternative strategies that depend on specific market conditions, managed futures have demonstrated an ability to generate returns in both bull and bear markets.
Key Characteristics of Managed Futures:
- Uncorrelated Returns: Trend-following strategies often perform independently of stock and bond markets.
- Global Exposure: Managed futures can take long and short positions across equities, bonds, currencies, and commodities.
- Crisis Alpha: Historically, managed futures have delivered positive returns during market drawdowns.
Key Takeaways for Advisors
- Finding persistent alpha in traditional equity markets is challenging, as highlighted by SPIVA and Morningstar research.
- Return stacking offers a structural way to pursue outperformance without sacrificing core equity exposure.
- Historical data suggests that a 100% stocks + 100% managed futures approach has improved returns and reduced drawdowns during crises.
- Managed futures provide an alternative return stream that has been uncorrelated to traditional equities and bonds.
Final Thoughts
As this strategy gains traction, return stacking has the potential to redefine how advisors think about diversification, return enhancement, and risk management, providing institutional-quality solutions in an accessible format.