Return Stacking in an Inverted Yield Curve Environment
Overview
If the cost of borrowing is driven by the yield of short-term Treasury Bills, does it make sense to stack bonds in an inverted yield curve environment? In this article, we share four key points as to why we believe the answer is a resounding “yes”.
Key Topics
Leverage, Return Stacking, Portable Alpha, Cost of Financing, Yield Curve, Inversion
When we first started publicly writing and talking about capital efficiency in 2017 – the predecessor conversation to return stacking, a modern evolution of portable alpha strategies – the 13-week U.S. Treasury Bill rate sat around 1.30%. Both approaches aim to enhance portfolio returns by layering additional return sources on top of a core portfolio without altering the overall asset allocation. By focusing on capital efficiency and diversification, return stacking builds upon these principles, allowing investors to seek excess returns while maintaining their desired risk exposure.
The prototypical example at the time was a 1.5x levered 60% stock / 40% bond portfolio (also referred to as a “90/60”). Such a portfolio would allow investors to achieve the exposure of a 60/40 using just two-thirds of their capital, freeing up valuable portfolio real estate for diversifying alternatives.
Implementing such a portfolio in practice was also trivial: for every $1 invested, $0.9 could be invested in stocks and $0.1 held aside as cash collateral for a $0.6 notional position in U.S. Treasury futures.
Figure 1: One Possible Implementation of a 90/60 Portfolio
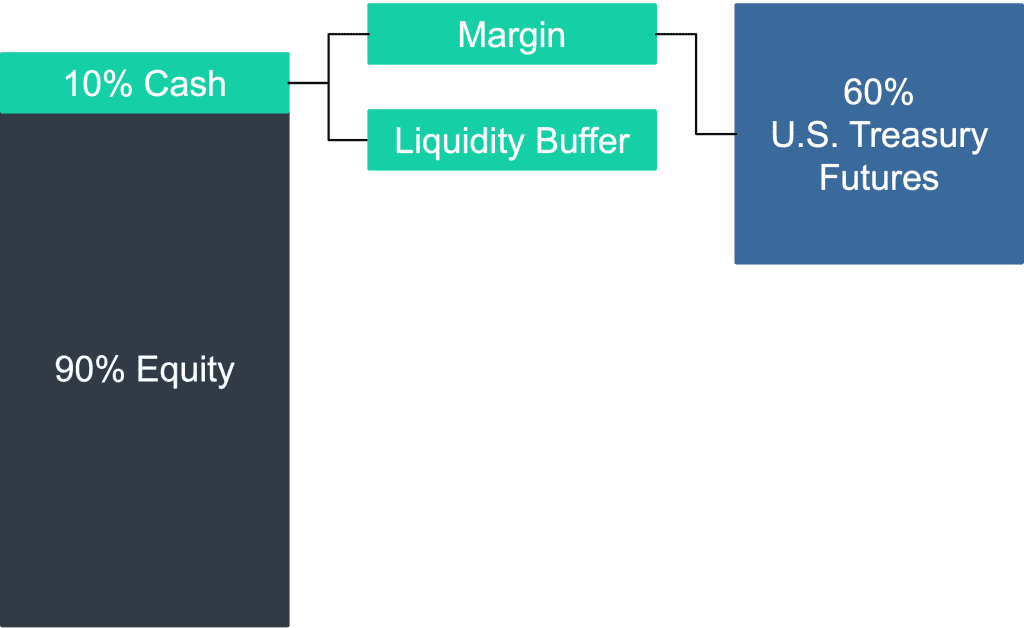
Source: Newfound Research.
Today, the 13-week Treasury Bill rate hovers near 4.5% and the yield curve is severely inverted, causing many to ask, “does return stacking still make sense, particularly if we use Treasury futures to achieve our leverage?”
We believe the answer is a resounding “yes”, with four key points to consider.
It’s the Portfolio, Not the Asset
With the yield curve severely inverted, paying short-term financing costs to invest in long-term Treasuries to achieve our leverage may seem like a losing prospect. However, as we’ve discussed, this line of thinking overlooks the principles of portable alpha, where we separate beta (market exposure) from alpha (active management returns) to construct more efficient portfolios.
By replicating beta through capital-efficient instruments like futures or swaps, we can free up capital to pursue uncorrelated alpha sources. Similarly, return stacking allows for layering additional strategies on top of a core portfolio, enhancing potential returns without fundamentally changing the asset allocation.
Using U.S. Treasury futures is simply a means to an end. Sticking with our 90/60 example, what we actually care about is achieving 1.5x levered 60/40 exposure and the flexibility that creates for us in portfolio construction.
Would we have the same concern about an inverted yield curve if for every $1 invested we purchased $0.60 of U.S. Treasuries and held $0.40 in cash as collateral for $0.90 in S&P 500 futures exposure? What if we simply borrowed money to lever an entire 60/40 portfolio up 1.5x?
Figure 2 plots the annual returns of these three different approaches. We can see that they are nearly identical to one another.
Figure 2: Annual Returns for Varying Approaches to Implementing a Levered 60/40 Portfolio
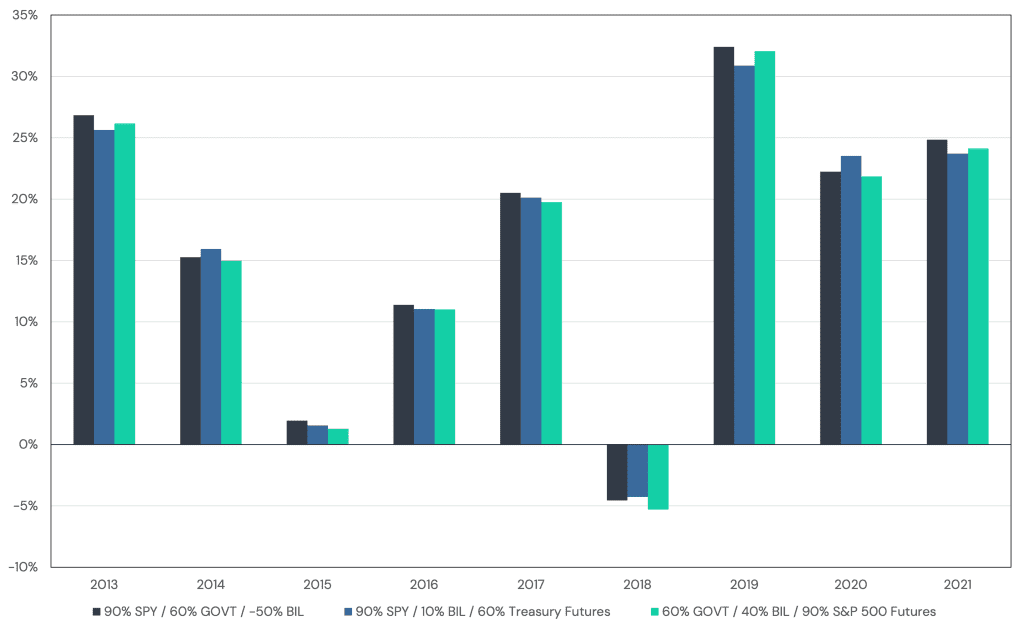
Source: Tiingo, Bloomberg, Barchart. Calculations by Newfound Research. Past performance is backtested and hypothetical. Returns are gross of all fees, costs, and taxes except for underlying expense ratios. Returns assume the reinvestment of all distributions. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Starting date based upon the availability of pricing data.
To draw this point out further, consider the case of explicitly borrowing money to lever the 60/40 portfolio up 1.5x and the following ways we could implement this portfolio:
- Hold 90% in stocks, 10% in U.S. Treasuries, and borrow to buy another 50% in U.S. Treasuries;
- Hold 60% in U.S. Treasuries, 40% in stocks, and borrow to buy another 50% in stocks;
- Hold 60% in stocks, 40% in U.S. Treasuries, and borrow to buy another 30% in stocks and 20% in U.S. Treasuries.
Figure 3: Different Approaches to Creating a 90/60 Portfolio
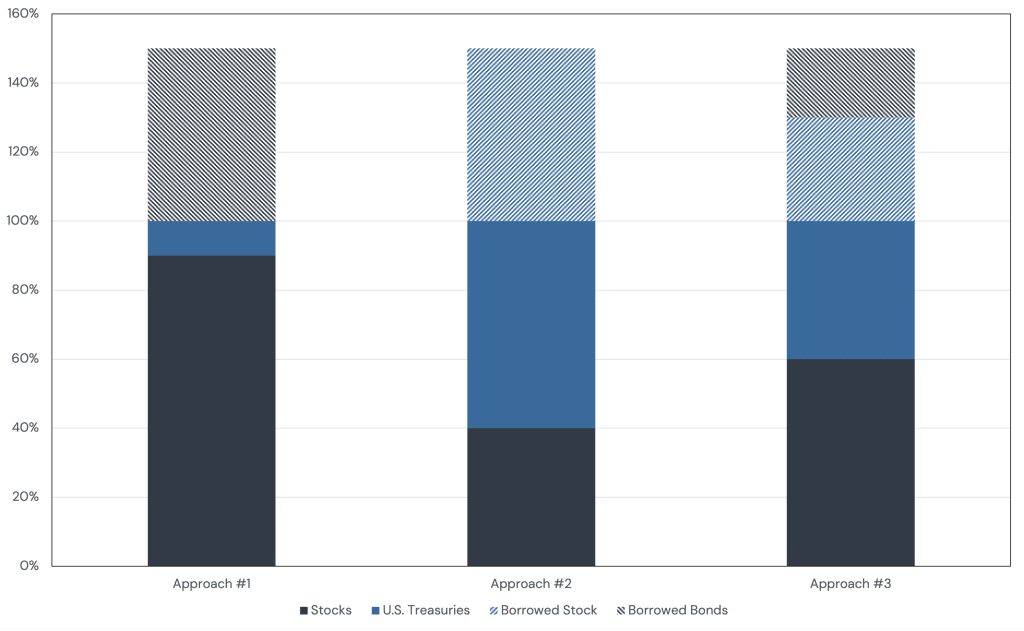
Does it matter which we choose? Does an inverted yield curve make the first choice less attractive than the second?
In theory, we should be indifferent to these choices. If we are concerned about using U.S. Treasury futures to achieve a levered 60/40, we should be equally concerned about using equity futures (“invert, always invert!”).
Register for our Advisor Center
Tools Center:
Easily backtest & explore different return stacking concepts
Model Portfolios:
Return stacked allocations, commentary and guidance designed
for a range of client risk profiles and goals
Future Thinking:
Receive up-to-date insights into the world of return stacking theory and practice
Sourcing Cheap Leverage
In practice, we do care how we implement a return stacked® portfolio. Not because the yield curve is inverted, but because explicitly borrowing at the short-term Treasury Bill rate is difficult for all but the largest institutions.
Treasury futures have historically allowed us to do just that, giving us a very cost-effective source of leverage. This capital efficiency is crucial in strategies like portable alpha, where we use derivatives to optimize portfolio construction. Figure 4 plots the embedded cost of leverage in 10-Year U.S. Treasury Futures relative to 3-Month U.S. Treasury Bill rates. By contrast, at the time of this writing, the current base margin rate is 10.75% at Schwab, 11.33% at Fidelity, and 12.50% at TD Ameritrade.
Figure 4: Embedded Financing Cost in 10-Year U.S. Treasury Futures versus 3-Month U.S. Treasury Bill Rate
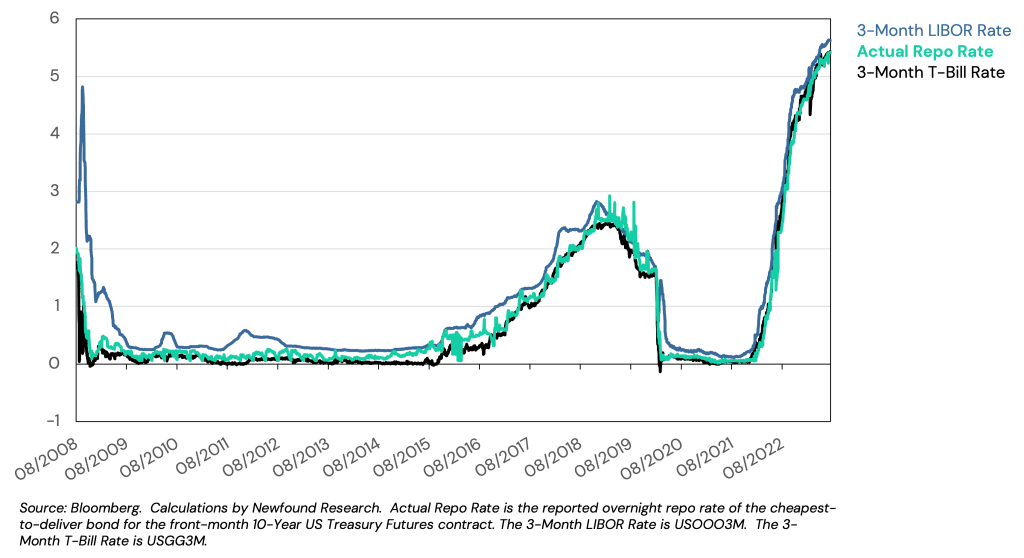
Source: Bloomberg.
It’s the Excess Returns that Matter
But what about the fact that short-term rates have climbed from near-zero to north of 4%? Is leverage now unattractive because the cost of financing is so high?
Let us return, for a moment, back to basic portfolio theory which says the expected return of an asset can be decomposed into two parts: the risk-free rate and the asset’s risk premium. For example, the expected return of stocks should be equal to the risk-free rate plus the equity risk premium (“ERP”). Similarly, the expected return of bonds should be equal to the risk-free rate plus the bond risk premium (“BRP”).
Figure 5: Decomposing Expected Returns into the Risk-Free Rate and Risk Premia
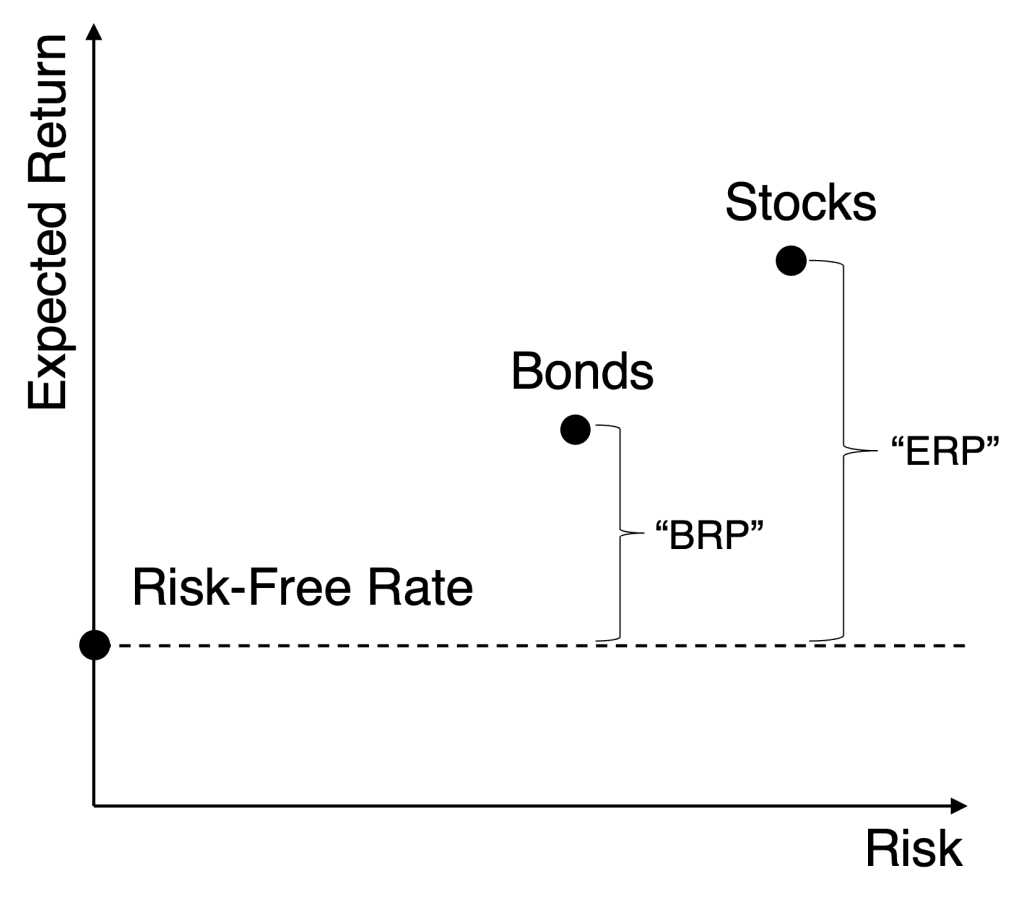
60% ERStocks + 40% ERBonds
Which can be decomposed as:
60% (Risk-Free Rate + ERP) + 40% (Risk-Free Rate + BRP)
Which equals:
60% ERP + 40% BRP + 100% Risk-Free Rate
Similarly, the 90/60 portfolio becomes:
90% ERP + 60% BRP + 100% Risk-Free Rate
= 1.5x (60% ERP + 40% BRP) + 100% Risk-Free Rate
What about a 30% Stock / 20% Bond / 50% Cash portfolio? No surprise:
30% ERP + 20% BRP + 100% Risk-Free Rate
= 0.5x (60% ERP + 40% BRP) + 100% Risk-Free Rate
Whether we’re holding cash, fully invested, or levered, all we are doing is scaling the risk premium exposure! It is the return in excess of the risk-free rate that matters.
The important implication here is that if we believe the levered portfolio is unattractive to invest in, it must also mean we believe the unlevered portfolio is unattractive to invest in.1 If 60% ERP + 40% BRP is negative, no amount of scaling up or down will change it; we’d be better off just holding cash.
How Inefficient is the Market?
None of this negates the fact that an investor may hold the active view that intermediate-to long-term U.S. Treasuries are unattractive to hold relative to cash today. Such a view, however, is not unique to a levered portfolio: it would affect levered and unlevered portfolios alike. To remain consistent with such a view, an investor should sell down their long-duration bonds in preference for short-duration exposure, regardless of leverage.
The only point we will stress here is that we believe the prudent approach is to assume, as a null hypothesis, that markets are generally efficient. After all, if everyone held the same active view that long-duration bonds are currently unattractive, they would sell those bonds, driving up the yield until the point they are attractive. If we believe markets are generally in equilibrium, the current long-term yield should be equally attractive as the short yield when appropriately adjusted for their risks.
How can that be the case when the short-term rate is higher than the long-term rate? The pure expectations hypothesis states that the yield curve embeds the expected path of short rates. It is important to remember that the expected return of a longer-dated Treasury should be compared to the expected return of a constantly rolled shorter-dated Treasury. An inverted yield curve, then, expresses the aggregate view that short rates should be lower in the future, which would bring down the return of the constantly rolled short-rate series.
Nevertheless, if an investor does have an active view about the relative expected returns of short-versus longer-dated Treasuries, that view would be expressed regardless of whether the portfolio is levered or not.
Conclusion
In this note, we have addressed the question whether return stacking still makes sense when the cost of financing increases, particularly when accessing that financing through longer-dated Treasury futures during an inverted yield curve environment.
We believe the answer is ‘yes’, and four key points help illustrate this fact. First, philosophically, we care less about the specific asset we are leveraging than the make-up of the levered portfolio. Second, in practice, we aim to choose an asset to lever that provides us with a cost of financing as close to the risk-free rate as possible. Third, it is the return in excess of the risk-free rate that ultimately matters. Finally, an active view about the relative attractiveness of Treasuries applies regardless of whether the portfolio is levered or not.
Embracing Portable Alpha in Return Stacking
By integrating the principles of portable alpha into return stacking, we can potentially enhance returns and may achieve greater diversification without significantly altering our core asset allocations. Leveraging capital-efficient instruments and layering uncorrelated strategies enable us to navigate inverted yield curves and other market anomalies more effectively.
More than anything, it’s the net portfolio allocation that matters.
1 This assumes that leverage is applied proportionally across the portfolio. If the unlevered portfolio is unattractive, leveraging it won’t change its fundamental characteristics.
